Plastic moulding is the process of pouring liquid plastic into a certain container or mould so that it hardens in that customized shape. These plastic moulds can then be used for a wide range of purposed. There are 5 types of plastic moulding that is considered to be the most effective and most popular.
These 5 types are extrusion moulding, compression moulding, blow moulding, injection moulding and rotational moulding. We will look at the details pertaining to each of these methods so that you can decide which one will be the most effective for you to use.
1. Extrusion Moulding
With extrusion moulding, hot melted plastic is pressed through a shaped hole to create a lengthy shaped plastic part. This customizable shape that the liquid plastic gets pressed through is called a die. This die is custom made for the particular outcome that is desired. It is almost like pressing dough through a press to make shaped cookies.
The other forms of plastic moulding also use extrusion so get the raw liquid into the moulds, the difference here is that other methods use the moulds to make the desired shape and here the extrusion itself is making the shape with the use of the die’s shape.
Common Uses of Extrusion Moulding
When using this method your outcome product will continuously have the same shape along the length of it. These can be things like straws or PVC pipes. These types of parts can be made at very high volumes because it can just keep producing the same shape without end.
In comparison, this type of moulding is low cost because the equipment is fairly simple and can have high productivity. The downside to this method is that you are very boxed in when it comes to the variety of parts you can make.
2. Compression Moulding
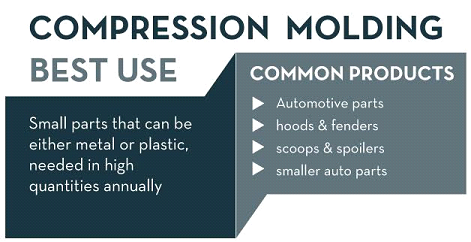
This method involves the raw liquid plastic being poured into a heated mould and then being compressed together to form the desired shape. The high temperature of the entire process ensures good strength in the final product. The process is finished off by cooling the liquid plastic so that it keeps its form before being trimmed and removed from the mould.
Common Uses of Compression Moulding
The most effective use for this method is when you want to make plastic replacement parts for broken metal parts. The reason for this is because the high-temperature method makes for a very strong and durable end product. Even though it is plastic, it is a strong and low-cost replacement for the metal parts.
The cost-effectiveness of this moulding method depends on factors like the complexity of the design, the number of
cavities and the surface finish. When you are mass producing then this method is ideal because the cost per part will be very low.
3. Blow Moulding
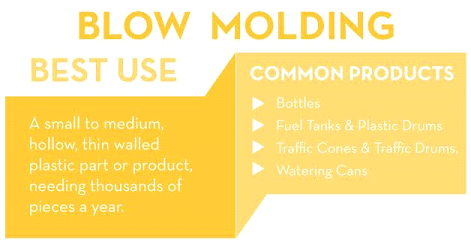
With blow moulding, the custom plastic parts come out hollow and thin-walled. This method is ideal for when the plastic part has to have uniform wall thickness. This is very similar to the process of glass blowing.
The machine heats up the raw plastic until it becomes liquid and then injects air into it like a balloon. The plastic is blown into a shaped mould and as it gets bigger it presses against the mould walls and it starts to take its shape. After the liquid balloon fills the mould it is cooled to keep its shape. The process is very fast and can produce up to 1400 pieces in a 12-hour work day.
Common Uses for Blow Moulding
Blow Moulding is mostly responsible for producing products like plastic bottles, drums, cases and even fuel tanks. If your required number of parts is around the hundreds of thousands then this method is perfect for you (like a soda company).
This is a fast and economical friendly option with the mould prices ranging somewhere in between injection moulding and rotational moulding.
4. Injection Moulding
Injection Moulding is fairly similar to extrusion moulding. The difference here is that with injection moulding the melted plastic is injected directly into a custom mould. The injection is under high pressure so that the mould is filled and a solid part is made. As with the other methods, after the mould is filled, the plastic is cooled as to keep its new shape and then the mould is opened.
This can be compared to a Jello mould when the mould is filled and then cooled to create the final product.
Common Uses for Injection Moulding
This is a common method to produce a high volume of plastic parts like car parts or even parts for surgical applications. Products can also be made with increased flexibility to suit the needs of designers or engineers.
When it comes to the pricing the moulds can be very expensive because they need to be steel or aluminium for higher strength and durability. Luckily, as with most methods, the cost per unit drops drastically depending on your production volume.
It is also worth noting that tooling can take up to 16 weeks and production up to 4 weeks.
5. Rotational Moulding
Also sometimes called rotomoulding, this method involves the resin or liquid being placed inside the mould and then being rotated at high speeds. The liquid then evenly covers the entire surface of the mould to create a hollowed part with all the walls evenly thick. After the mould is cooled and the liquid plastic has taken its new form it is then taken out of the mould.
This method is very material efficient and very little goes to waste making it more economical and environmentally friendly.
Common Uses for Rotational Moulding
The most common use for this method is for big and hollow parts. These parts include car parts, bins, kayaks, road cones, pet houses and storage tanks.
The moulds that are used in rotational moulding are highly intricate to make products customizable and changeable. This can include things like special inserts and curves as well as logos and slots. These can be placed into the mould to change the final product.
The tooling costs with rotational moulding are lower than other methods like injection and blow moulding. This makes for lower start-up costs and more effective production costs even at low volume production.